Introduction
In IPF research, the term “BIPF mouse” often appears. For newcomers or cross-disciplinary readers, it can be confusing: is it a specific transgenic line, or a model acronym?
In fact, the BIPF mouse is not a transgenic strain name, but the acronym for the Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis model. This article provides an overview of the model’s definition and value, highlights its link to the protective gene ISM1, and outlines how to leverage RDDC resources.
What Is the BIPF Mouse: A Classical Induction Model
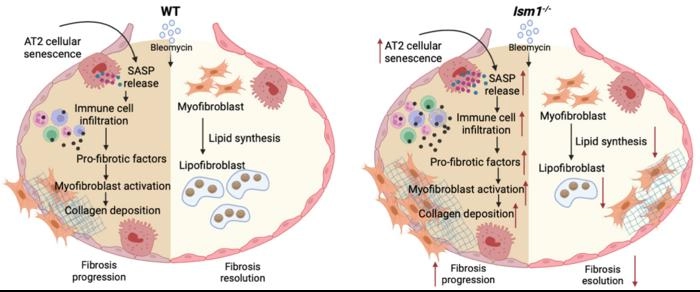
“BIPF” stands for Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. The model induces a fibrosis phenotype by delivering bleomycin via intratracheal instillation or intraperitoneal injection. It is a widely used, validated, and standardized gold-standard animal model.
- Induction: bleomycin generates reactive oxygen species, causing alveolar epithelial cell injury and apoptosis.
- Secondary response: dysregulated “repair” over-activates fibroblasts and promotes ECM deposition.
- Final phenotype: excessive collagen in the interstitium leads to structural damage and impaired gas exchange, mirroring human IPF.
Why It Became a Standard
- Reproducibility and control: dosing, timing, and routes are easily standardized.
- Pathology coverage: spans acute inflammation, active fibrosis, and late-stage fibrosis.
- Drug screening value: multiple approved agents validated preclinically in BIPF.
BIPF and ISM1: The Key Mechanistic Link
ISM1, secreted by AEC2 cells, restrains fibroblast activation as a “brake.” In BIPF, injury reduces ISM1 secretion, removing the brake and sustaining fibrosis. Exogenous ISM1 reverses progression in the model.
Research Workflow: Platform-Powered Practice
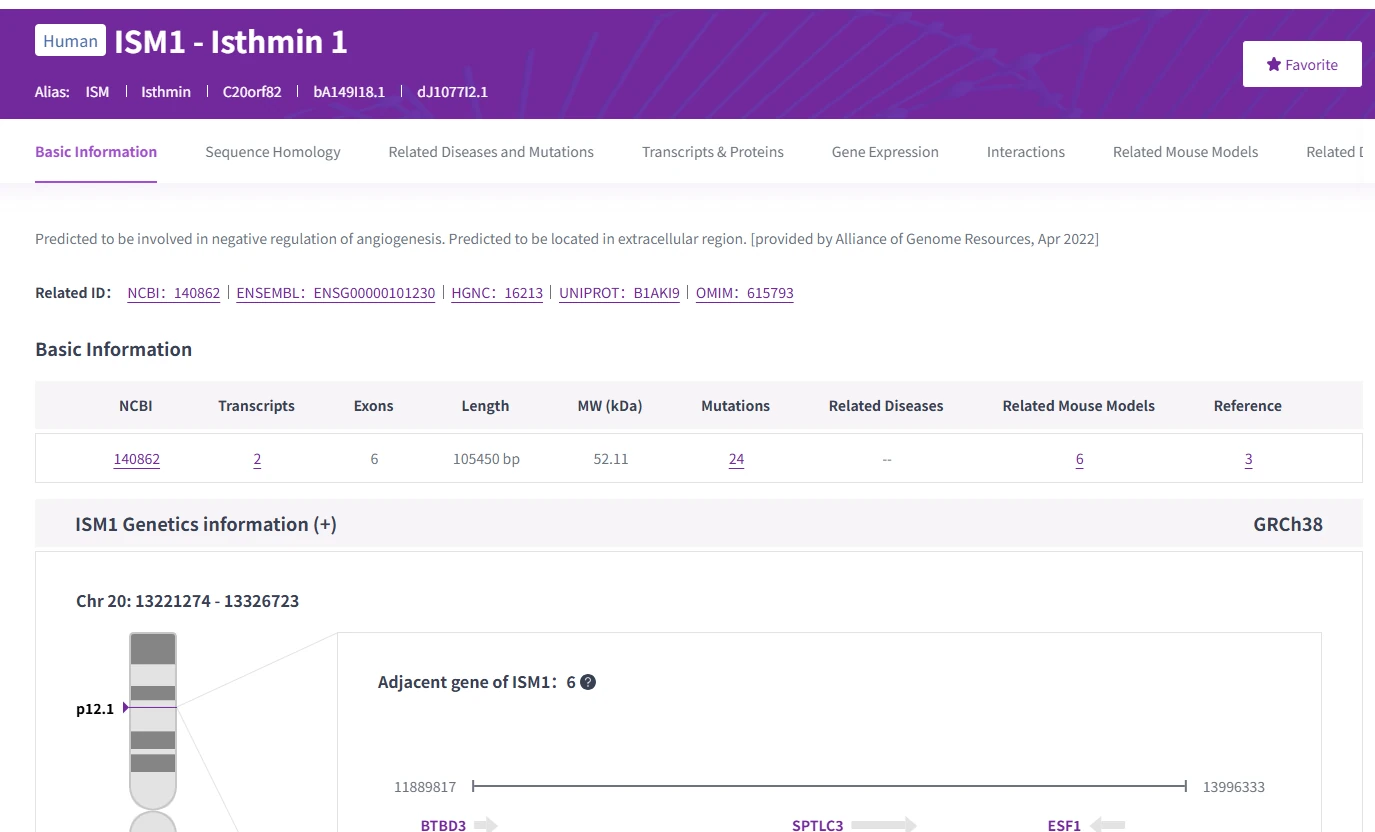
Target anchoring: consolidate ISM1 structure, transcripts, sequences, functions, and literature.
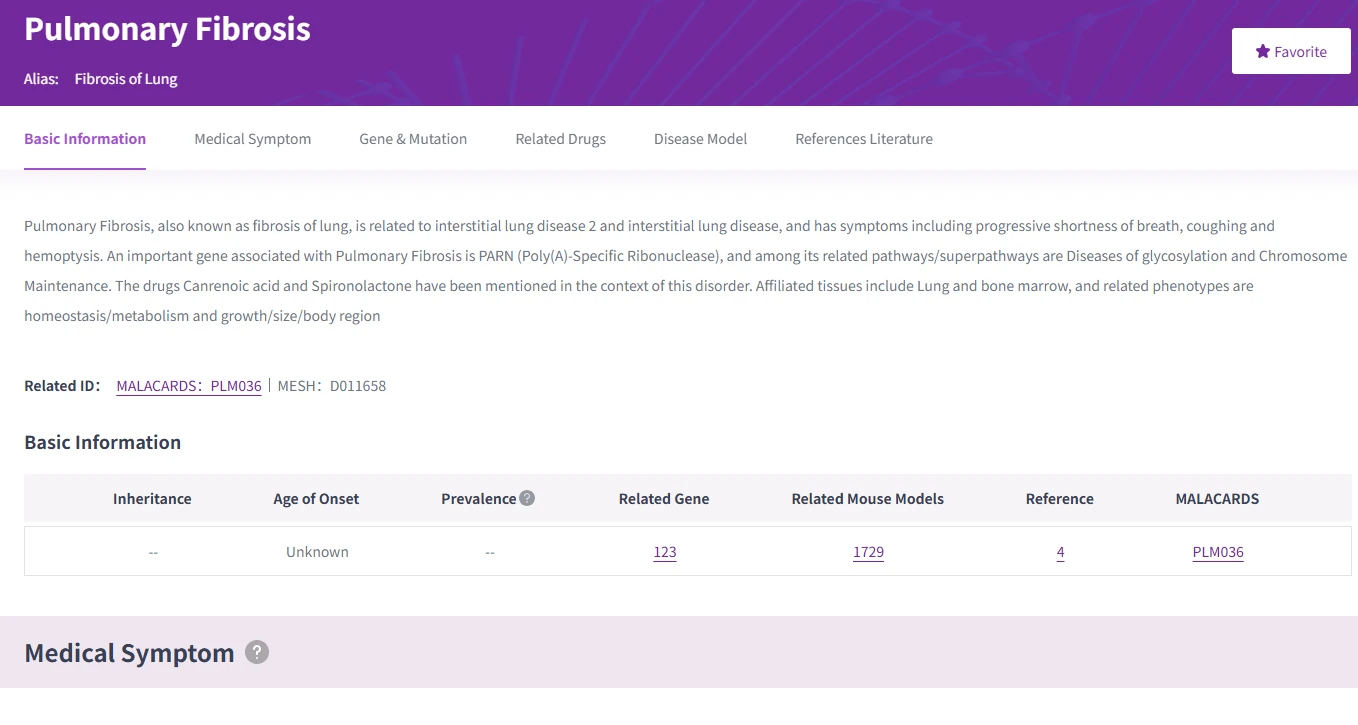
Disease linkage: query ISM1 associations to guide safety and repurposing.
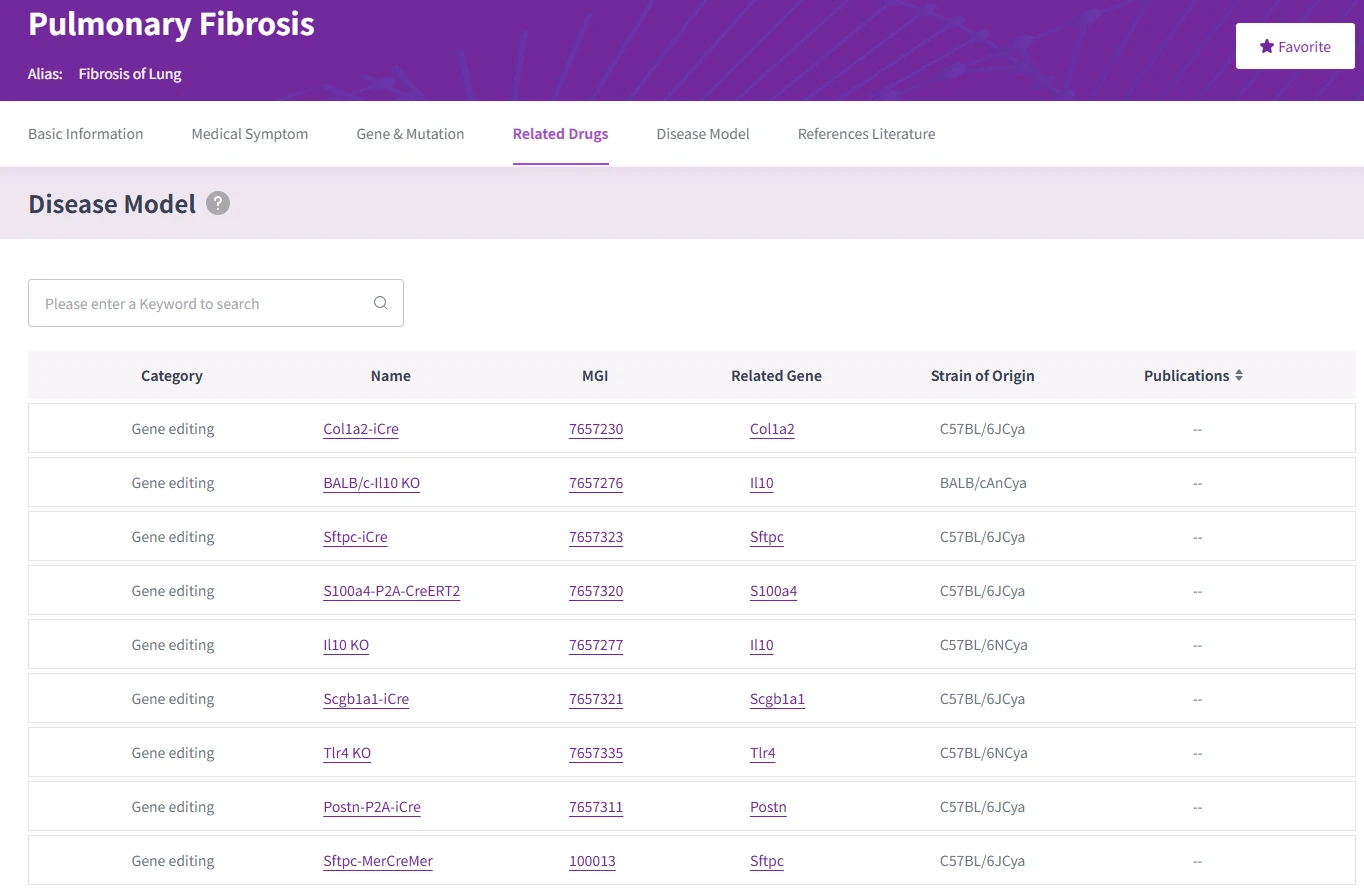
Model comparison: retrieve and contrast fibrosis models for optimal design.
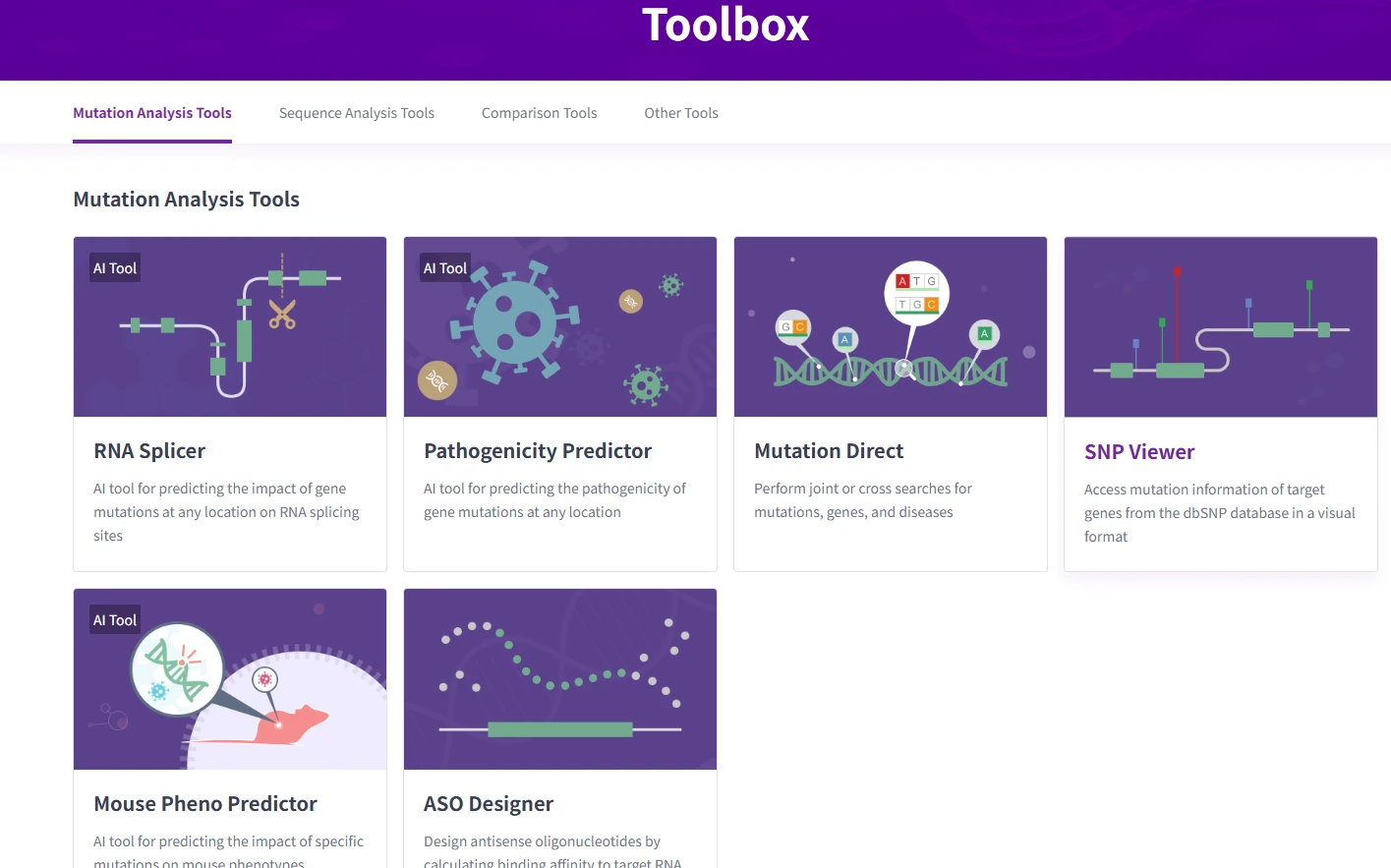
General tools: leverage sequence and pathway tools for analyses.
Conclusion
The BIPF model provides a robust experimental setting, while ISM1 offers an actionable mechanistic handle for validation and intervention.