Favorite
Pathogenicity Predictor
Predict genetic mutation pathogenicity instantly with our deep learning AI.
Please enter the mutation site in the following input box for prediction.
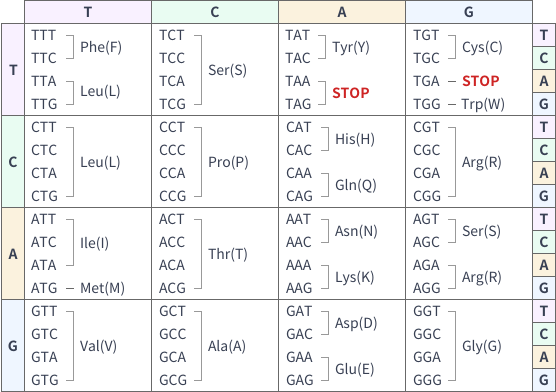
Codon Chart
Model Introduction
Tutorial (Video)
Tutorial (Text)
01
Why Use a Pathogenicity Predictor?
In genetic research and clinical testing, researchers and clinicians often face significant challenges:
Uncertainty about whether a specific gene mutation is pathogenic.
Time-consuming and error-prone manual analysis of literature and databases.
Complexity in handling different transcripts and mutation formats.
To address this, we developed the Pathogenicity Predictor—an intelligent tool combining deep learning AI with bioinformatics databases (e.g., ClinVar, OMIM).
It automatically identifies and predicts the pathogenicity of human single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), including insertions and deletions.
No programming or complex configuration is required. In just a few steps, you get:
Pathogenicity classification (e.g., "Likely Pathogenic," "Benign")
A quantitative pathogenicity score (0 to 1)
Visualization of the mutation location and sequence
Optional RNA splicing prediction results
Whether you are a researcher, clinician, or educator, you can quickly obtain accurate and intuitive mutation analysis.
Try It Now
Please enter the mutation site in the following input box for prediction.
Codon Chart
01
Detailed Operating Steps
Step 1: Access the Tool Interface
Step 2: Input Mutation Information (Example: SOD1:c.335G>T)
The tool supports 4 input modes: Quick Paste, Manual Entry, Protein Prediction, and Transcript Prediction.
Advantage: Flexible input methods meet diverse research needs; inputs are parsed automatically.
Step 3: Enter Gene and Transcript Details (using "Protein Prediction" mode)
Enter "SOD1" in the "Gene Name" field. The system will auto-suggest matching genes to prevent spelling errors.
The system defaults to the most common transcript (e.g., SOD1:NM_000454.5), or you can select other versions from the dropdown menu.
Advantage: AI automatically recommends the most appropriate transcript, eliminating manual searches.
Step 4: Input Mutation Site Information
Enter the mutation info, e.g., "c.335G>T", in the "Protein Coordinate" field.
The system automatically parses the corresponding amino acid change (e.g., position 112 Cys:TGC).
Click [Expand Diagram] to view the mutation's position in the gene structure (intron/exon boundaries).
Advantage: The mutated base is automatically color-coded, providing an intuitive visualization of its location.
Step 5: Add or Submit Mutations
Use [Add Mutation] to submit multiple sites at once (up to 5).
Click [Submit] to start the AI prediction.
A real-time progress bar will display. Prediction time varies by the number of mutations.
Step 6: View Prediction Results
Clinical Significance: The AI provides a classification (e.g., "Likely Pathogenic," "Uncertain," "Benign") based on ClinVar, OMIM, and internal models.
Pathogenicity Score: Displays a 0-1 probability (e.g., 0.6321 = 63.21% chance of pathogenicity).
Sequence Details & Visualization: The mutation site is highlighted. Compare pre- and post-mutation amino acid sequences.
RNA Splicing Prediction: If checked, you can also see the mutation's impact on splice sites and its corresponding score.
Advantage: Integrated, multi-level results, from pathogenic classification to mechanistic analysis.
Step 7: Export and Save Results
Supports saving as a screenshot or exporting results to your local drive / email.
Advantage: Convenient for research notes, report writing, or sharing with your team.
Try the Pathogenicity Predictor now and simplify genetic prediction!
Please enter the mutation site in the following input box for prediction.
Codon Chart
01
Application Scenarios
Research
Explore pathogenic mechanisms and functional effects of disease-related mutations.
Example
Study the potential pathogenicity of a candidate mutation in a rare disease.
Clinical
Assist in interpreting genetic reports and assessing pathogenicity based on ACMG guidelines.
Example
Quickly differentiate pathogenic mutations from benign variants in genetic testing.
Education
Dynamically demonstrate the impact of mutations on protein structure and function.
Example
Show amino acid changes and splicing abnormalities in a classroom setting.
Industry
Filter high-frequency benign mutations during drug R&D or target screening to improve analysis accuracy.
Helpful Tips
Gene Name Format
Use standard symbols (e.g., "TP53" not "p53"). You can confirm via NCBI Gene.
Mutation Format
Must follow HGVS nomenclature (e.g., "c.123A>T" for coding region). Incorrect formats will fail to parse.
Transcript Selection
The MANE transcript is loaded by default. Please confirm it matches your sample source.
Batch Analysis
A maximum of 5 mutation sites can be submitted at one time. For larger batches, please submit in groups.
Helper Tools
A codon table is provided on the left. The (?) icon next to "Standard Mutation Name" provides a writing guide.
[CTA Button] Start Your Prediction Now
Start Your Prediction Now
Please enter the mutation site in the following input box for prediction.
Codon Chart
01
FAQ —— Pathogenicity Predictor | An AI-Driven Tool for Genetic Prediction
Q1What is the Pathogenicity Predictor?
It is a mutation pathogenicity prediction tool based on AI deep learning.
Q2Are the results reliable?
The results are stable and reproducible, combining data from ClinVar, OMIM, and our AI model.
Q3Does it require installation?
No installation is needed. It is a free-to-use web tool.
Q4Does it support batch analysis?
You can submit up to 5 mutations at a time. For larger studies, please input in batches.
Q5Who is this for?
Researchers, clinicians, students, and pharmaceutical R&D teams.
Other Useful Tools

Pathogenicity Predictor
AI tool for predicting the pathogenicity of gene mutations at any location
RNA Splicer
AI tool for predicting the impact of gene mutations at any location on RNA splicing sites
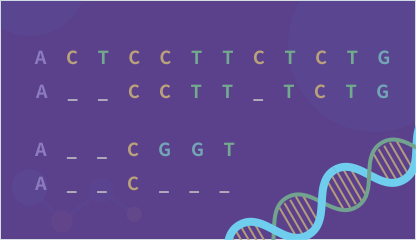
Sequence Alignment
Compare nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarities

Mutation Direct
Perform joint or cross searches for mutations, genes, and diseases