HIF-1α Hypoxia-Inducible Factor: From Nobel Prize Mechanism to Drug Research and Clinical Applications
HIF-1α serves as the master switch for cellular hypoxic responses, stabilizing and activating angiogenesis and metabolic reprogramming under hypoxic conditions. This article provides insights into its Nobel Prize-winning mechanism, molecular pathways, and drug development prospects for researchers, healthcare professionals, and patients.
Nobel Prize Mechanism Overview
In 2019, William G. Kaelin Jr., Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, and Gregg L. Semenza won the Nobel Prize for revealing how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability. The key mechanism involves: under oxygen-rich conditions, HIF-1α is hydroxylated by prolyl hydroxylases (PHD), recognized by Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein, and subsequently degraded; under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α stabilizes and enters the nucleus, initiating gene expression for angiogenesis and metabolic reprogramming.
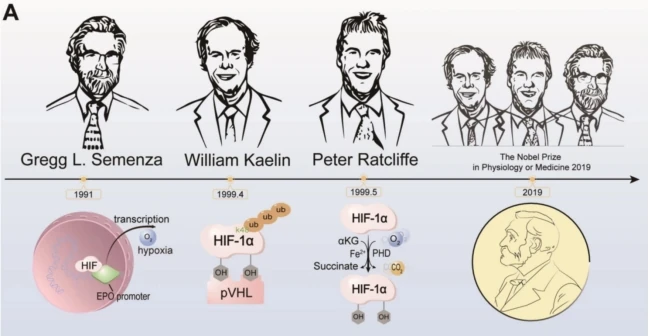
Molecular Pathways of Oxygen Sensing
The HIF-1 complex consists of HIF-1α and HIF-1β (ARNT). HIF-1α is responsible for oxygen-sensitive regulation and determines complex activity. Under hypoxic conditions, it upregulates VEGF and key glycolytic enzymes, promoting angiogenesis while reducing oxygen consumption, forming survival adaptation. This pathway serves as a common hub for tumor hypoxic microenvironments and tissue repair.
Click to use the Anti-tumor Drug Target Query Tool
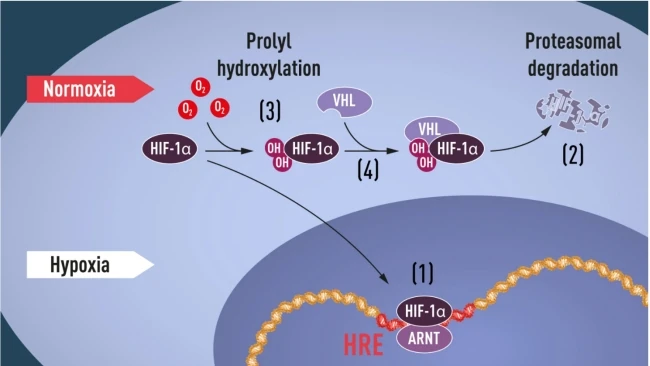
Clinical and Research Application Key Points
- Anemia and Ischemia: Moderate activation of HIF-1α may enhance EPO expression and tissue tolerance, improving anemia and myocardial ischemia.
- Tumor Microenvironment: Inhibiting HIF-1α can suppress angiogenesis and glycolysis, reducing tumor invasiveness and drug resistance.
- Reproduction and Metabolism: In conditions like PCOS with cryptic hypoxia, precise HIF-1α intervention may improve follicular development and metabolic balance.
- Age-related Diseases: Oxygen sensing imbalance may trigger chronic inflammation and metabolic inefficiency, suggesting the necessity for early assessment and intervention.
Gene Editing Models and Research Acceleration
Animal models are crucial for mechanism validation and drug efficacy evaluation. Gene-edited mice can be used for mechanistic research and candidate drug evaluation in scenarios including tumor hypoxia, cerebral and cardiac ischemia, anemia, and metabolic diseases.
| Product Name | Product Code | Full Strain Name | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hif1a-KO Mouse | S-KO-02449 | C57BL/6JCya-Hif1aem1/Cya | Hif1a Gene Knockout |
| Hif1a-flox Mouse | S-CKO-02890 | C57BL/6JCya-Hif1aem1flox/Cya | Conditional Gene Knockout |






