SIRT3-XBP1s-IL-23 Inflammatory Axis and TLR7/8 Pathway
SIRT3 is not only a mitochondrial deacetylase but can also enter the nucleus to deacetylate XBP1s, regulating TLR7/8-induced IL-23 and other core inflammatory factors. This article reviews mechanistic evidence, animal models, and potential therapeutic strategies for researchers and clinicians.
Mechanistic Core
- SIRT3 is a NAD+-dependent deacetylase traditionally localized in mitochondria; latest evidence shows it can enter the nucleus under stress conditions (IMQ stimulation).
- In macrophages, SIRT3 deacetylates XBP1s, reducing its transcriptional activity and inhibiting TLR7/8 axis-induced IL-23, IL-6, and TNF-α expression, alleviating psoriasis-like inflammation.
- This pathway reveals the possibility of mitochondria-nucleus cross-compartment regulation, providing new targets for upstream precision intervention.
Experimental Verification
Cellular Level
Immunofluorescence evidence shows that SIRT3 co-localizes with XBP1s in the nucleus after IMQ stimulation; inhibiting SIRT3 enhances XBP1s acetylation and transcriptional activity, while overexpressing SIRT3 reverses this effect.
Animal Level
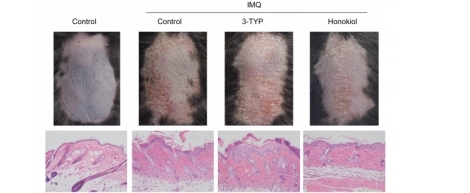
Sirt3 knockout (Sirt3-/-) mice customized by Cyagen Biosciences combined with IMQ-induced models show that Sirt3 deficiency exacerbates erythema, scaling, and skin thickening, with significantly elevated inflammatory factors; 3-TYP exacerbates while Honokiol alleviates pathological manifestations.
Clinical Samples
SIRT3 expression is decreased in macrophages from psoriasis patients and correlates with increased XBP1s acetylation.
Clinical and Drug Research Insights
Upstream Precision Intervention
As an activating target, enhancing SIRT3 activity is expected to downregulate XBP1s-mediated inflammatory pathways, complementing biologics and topical therapies.
Systemic Effects
Cross-compartment regulation suggests potential for multi-dimensional synergistic effects in metabolism, immunity, and skin barrier function.
Evaluation and Translation
It is recommended to conduct dose-response and safety evaluations combining animal models and patient samples to provide evidence for small molecule activators or gene therapy.
Gene Editing Models and Research Acceleration
For mechanistic research on psoriasis and immune metabolism, Sirt3 gene-edited mice can be used for IMQ models, Th17 axis evaluation, and candidate drug screening.
| Product Name | Product Code | Full Strain Name | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sirt3-KO Mouse | S-KO-11422 | C57BL/6NCya-Sirt3em1/Cya | Sirt3 Gene Knockout |
| Sirt3-KO Mouse | S-KO-11423 | C57BL/6JCya-Sirt3em1/Cya | Sirt3 Gene Knockout |
| Sirt3-flox Mouse | S-CKO-12758 | C57BL/6JCya-Sirt3em1flox/Cya | Sirt3 Conditional Gene Knockout |
| Sirt3-flox Mouse | S-CKO-17934 | C57BL/6NCya-Sirt3em1flox/Cya | Sirt3 Conditional Gene Knockout |
Selected Published Literature by Customers:
- Chen DQ et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(5):1038-1050.
- Guo M et al. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1128543.
- Jian Y et al. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(2):e13362.
- Li R et al. J Cell Physiol. 2023;238(9):2090-2102.
- Zhao J et al. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):594.






